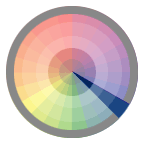
Monochromatic Relationship Colors that are shade or tint variations of the same hue.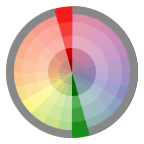
Complementary Relationship Those colors across from each other on a color wheel.
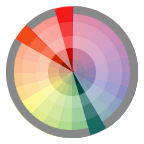
Split-Complementary Relationship One hue plus two others equally spaced from its complement.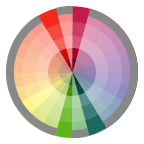
Double-Complementary Relationship Two complementary color sets; the distance between selected complementary pairs will effect the overall contrast of the final composition.
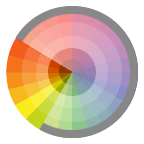
Analogous Relationship Those colors located adjacent to each other on a color wheel.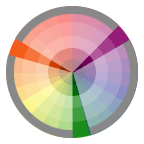
Triad Relationship Three hues equally positioned on a color wheel.
COLOR AND CONTRAST
If there is not a lot of contrast between colors( like yellow and white) it will be very hard to read. If there is a lot of contrast between vibrant colors, like blue and red it could cause illusions.The contrast of saturation
 The contrast is formed by the juxtaposition of light and dark values and their relative saturation.
The contrast is formed by the juxtaposition of light and dark values and their relative saturation.
The contrast of light and dark
 The contrast is formed by the juxtaposition of light and dark values. This could be a monochromatic composition.
The contrast is formed by the juxtaposition of light and dark values. This could be a monochromatic composition.
The contrast of extension
 Also known as the Contrast of Proportion. The contrast is formed by assigning proportional field sizes in relation to the visual weight of a color.
Also known as the Contrast of Proportion. The contrast is formed by assigning proportional field sizes in relation to the visual weight of a color.
The contrast of complements
 The contrast is formed by the juxtaposition of color wheel or perceptual opposites.
The contrast is formed by the juxtaposition of color wheel or perceptual opposites.
Simultaneous contrast
 The contrast is formed when the boundaries between colors perceptually vibrate. Some interesting illusions are accomplished with this contrast.
The contrast is formed when the boundaries between colors perceptually vibrate. Some interesting illusions are accomplished with this contrast.
The contrast of hue
 The contrast is formed by the juxtaposition of different hues. The greater the distance between hues on a color wheel, the greater the contrast.
The contrast is formed by the juxtaposition of different hues. The greater the distance between hues on a color wheel, the greater the contrast.
The contrast of warm and cool
 The contrast is formed by the juxtaposition of hues considered 'warm' or 'cool.'
The contrast is formed by the juxtaposition of hues considered 'warm' or 'cool.'
Keine Kommentare:
Kommentar veröffentlichen